Does A Binding Or Not Binding Price Floor Create Surplus
This is the currently selected item.
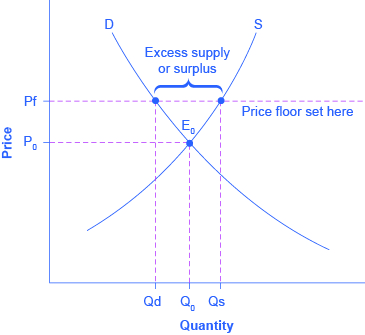
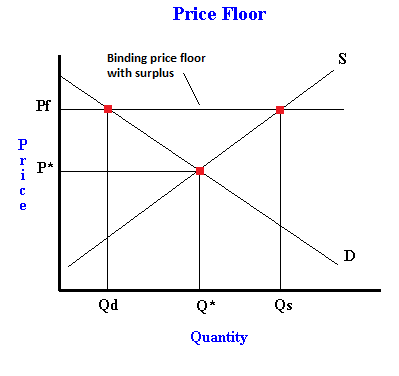
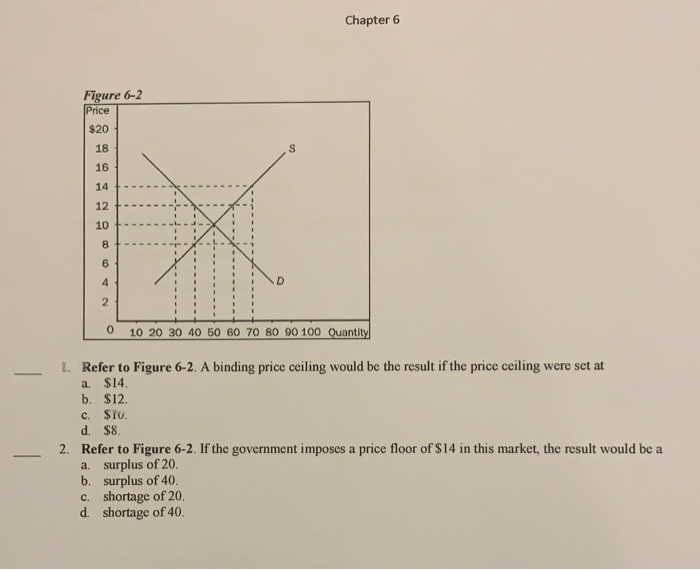
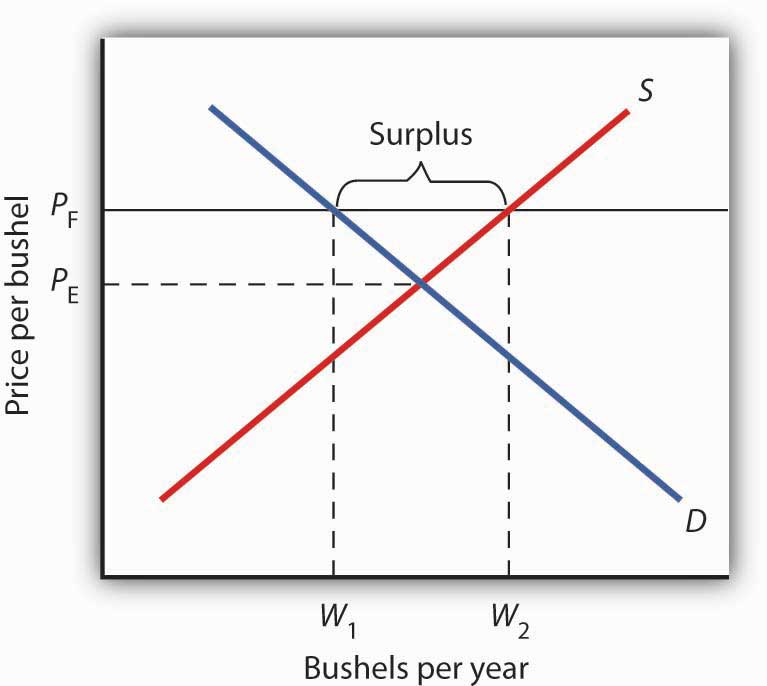
Does a binding or not binding price floor create surplus. Because the government requires that prices not drop below this price that. An effective binding price floor causing a surplus supply exceeds demand. How price controls reallocate surplus. The persistent unwanted surplus that results from a binding price floor causes inefficiencies that do not include.
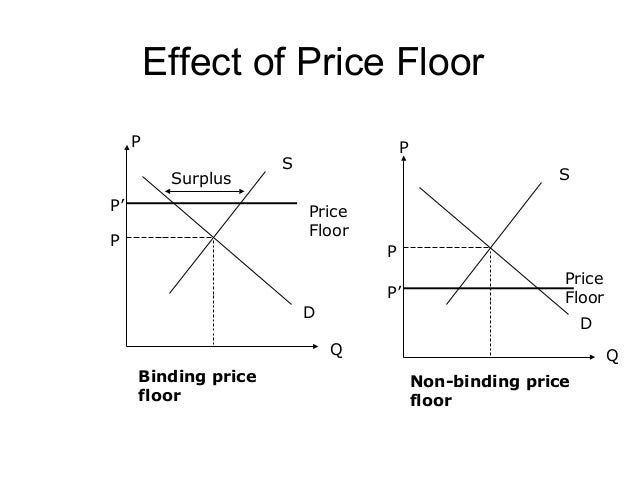
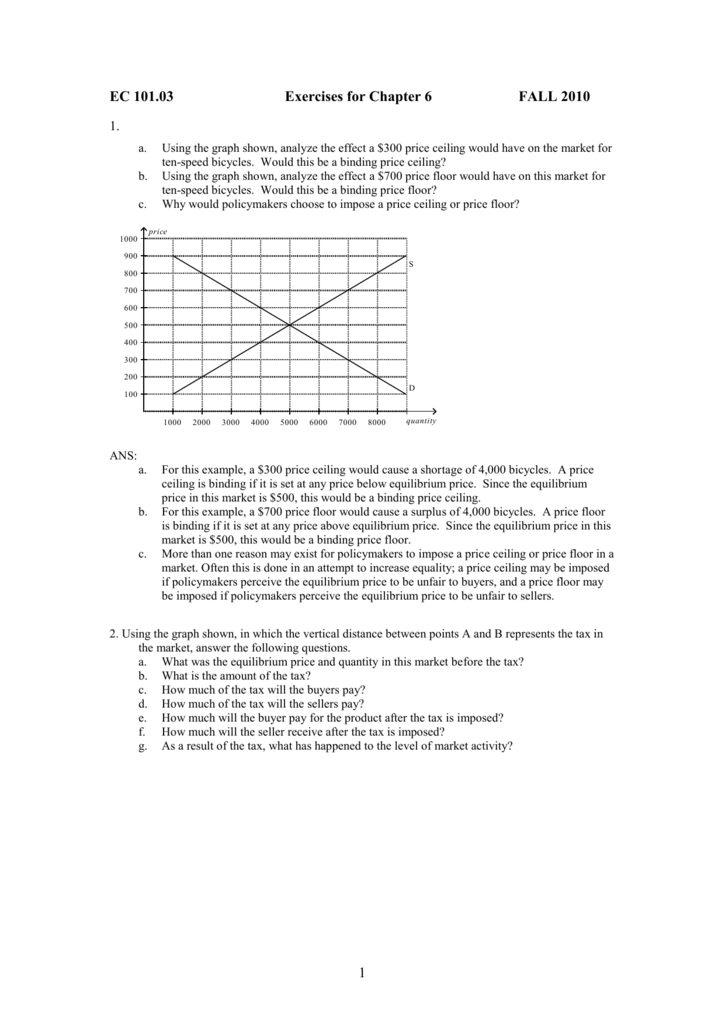
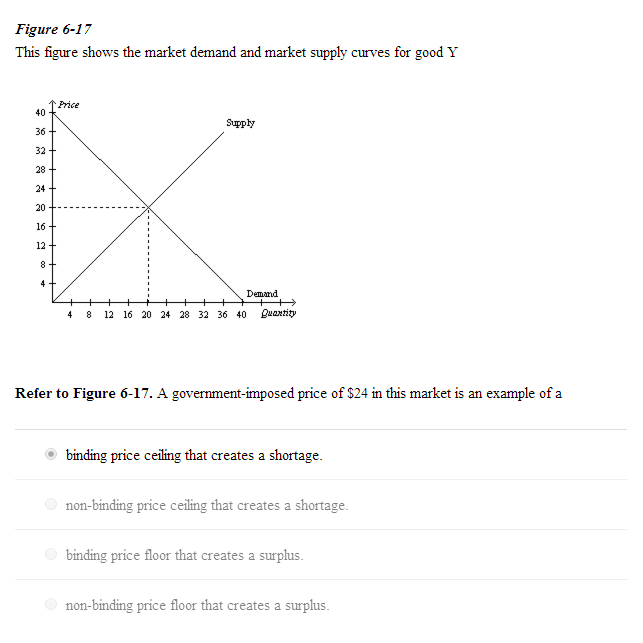
Types of price floors. Qd 19 6154 1 1538p rewriting. The latter example would be a binding price floor while the former would not be binding. The result is a quantity supplied in excess of the quantity demanded qd.
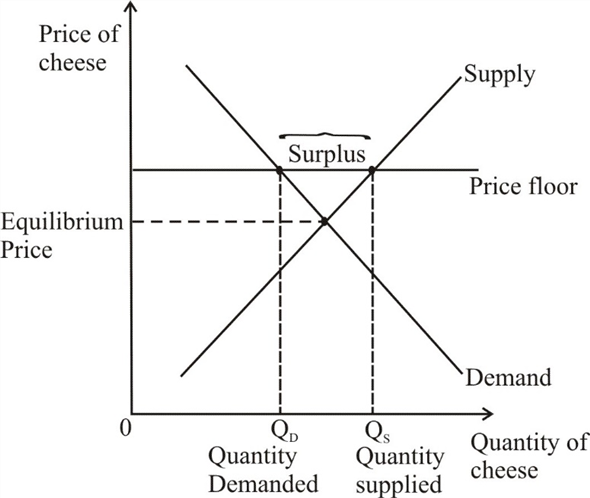
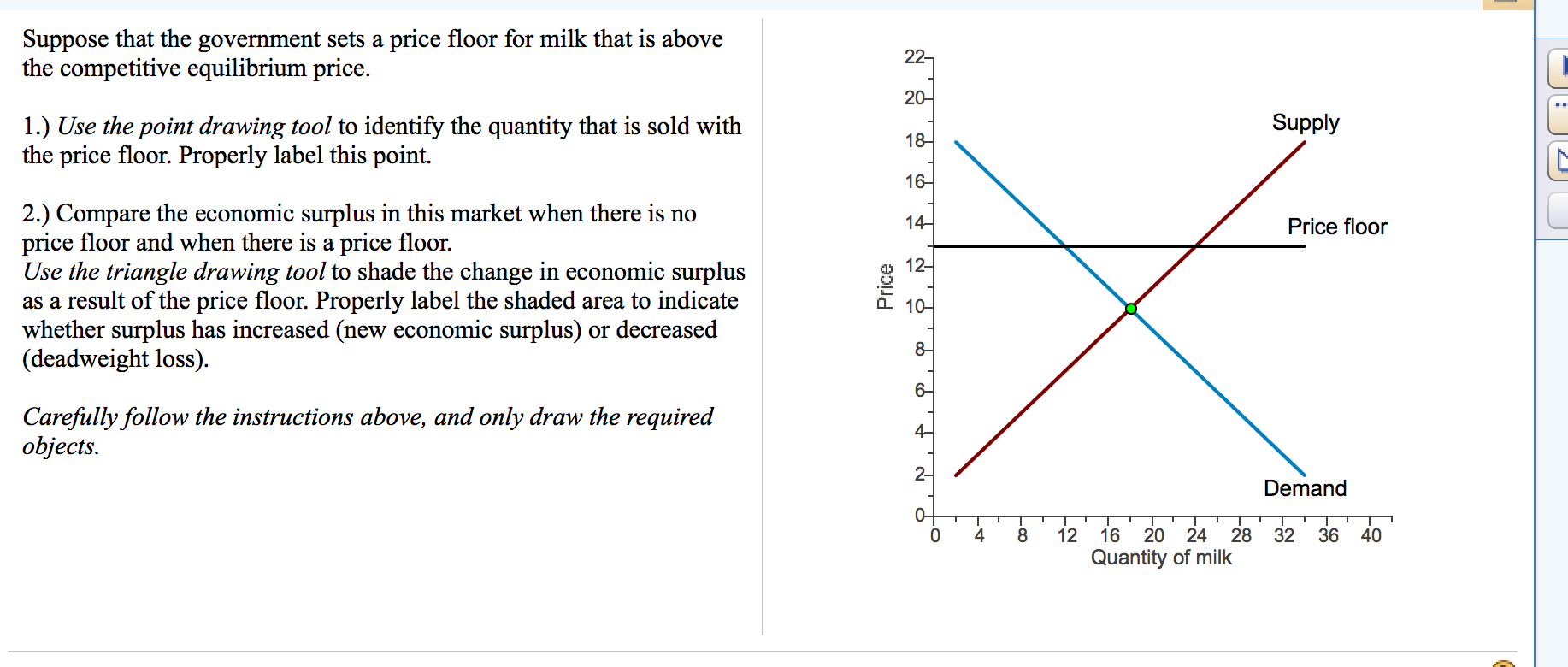
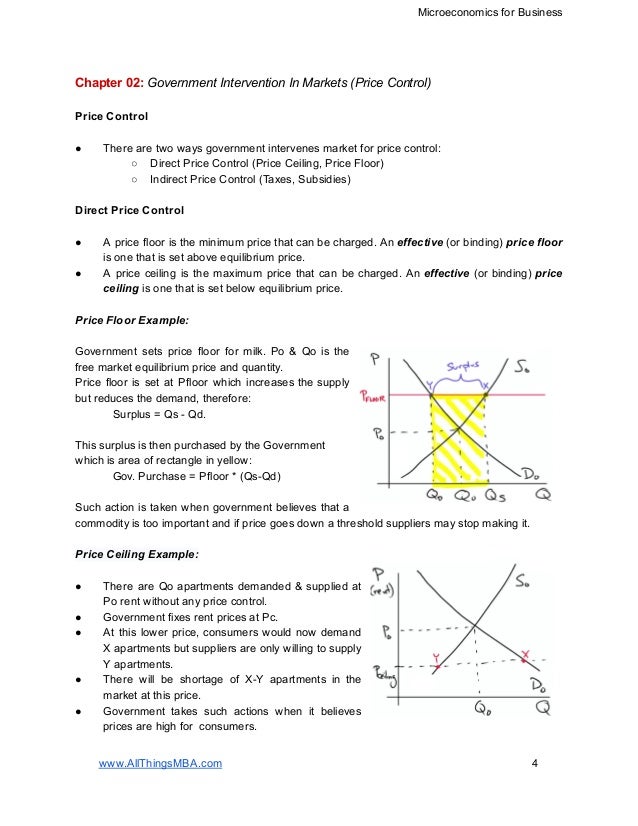
Price ceilings and price floors. Taxation and dead weight loss. Price floors set above the market price cause excess supply a price floor set above the market price causes excess supply or a surplus of the good because suppliers tempted by the higher prices increase production while buyers put off by the high prices decide to buy less. When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price as in this example it is considered a binding price floor.
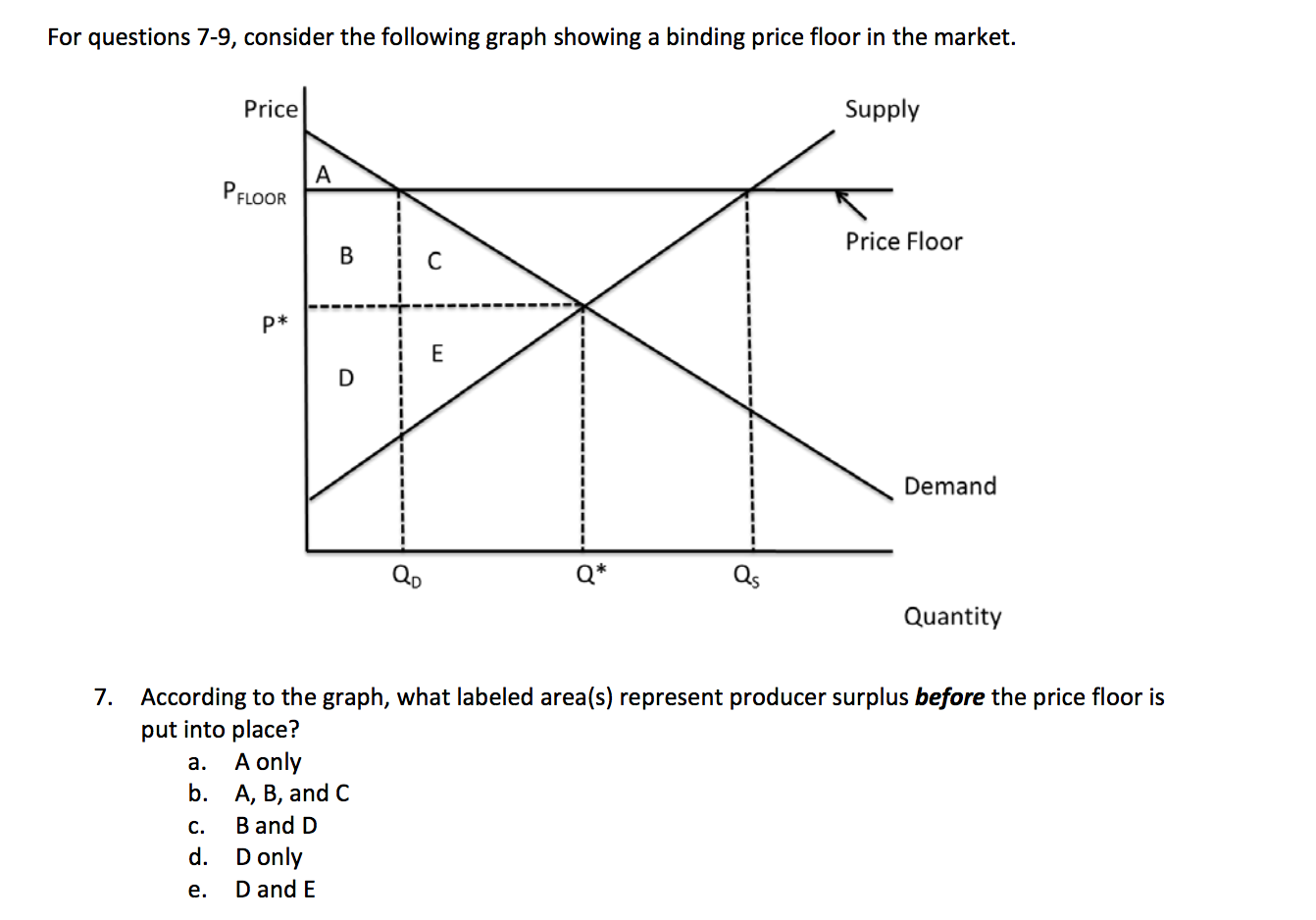
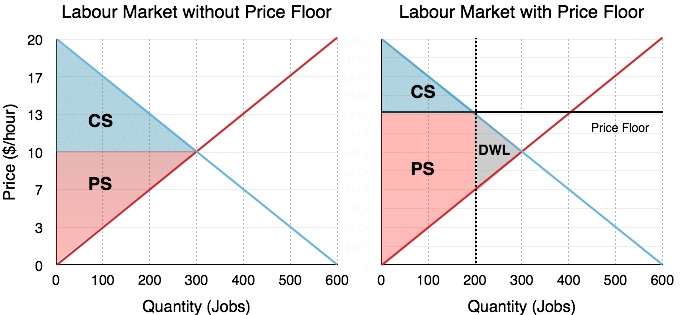
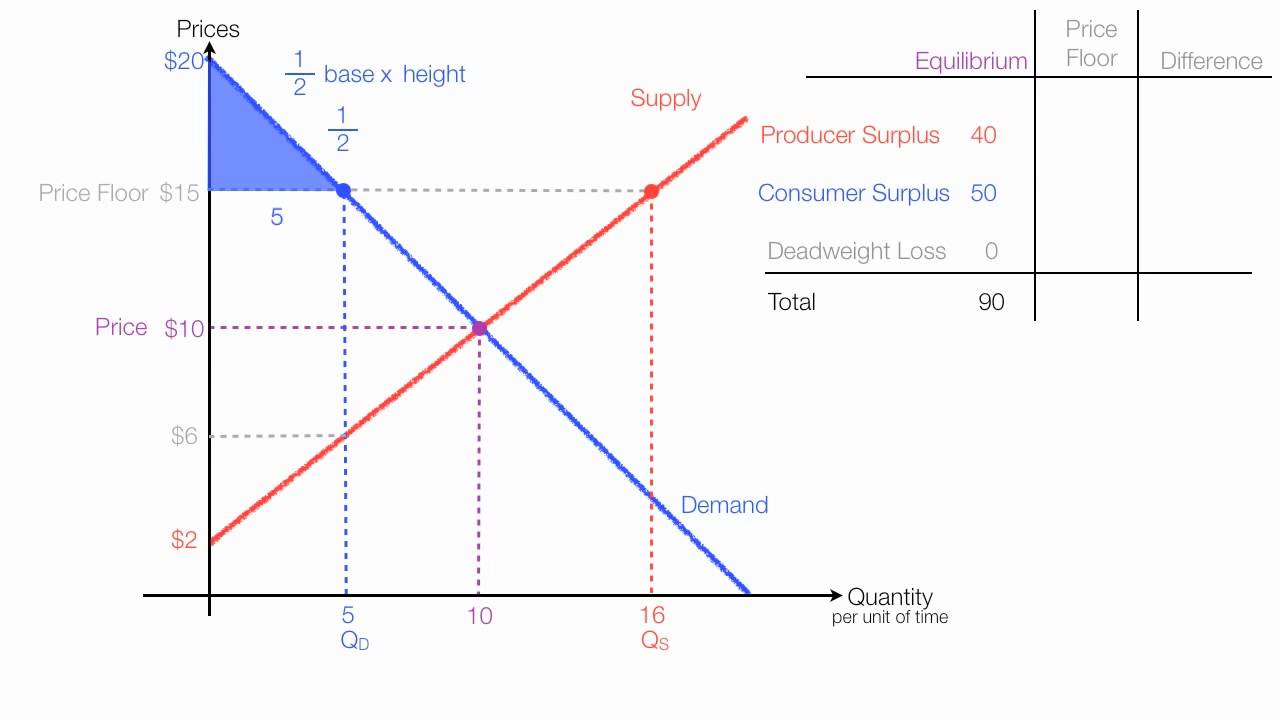
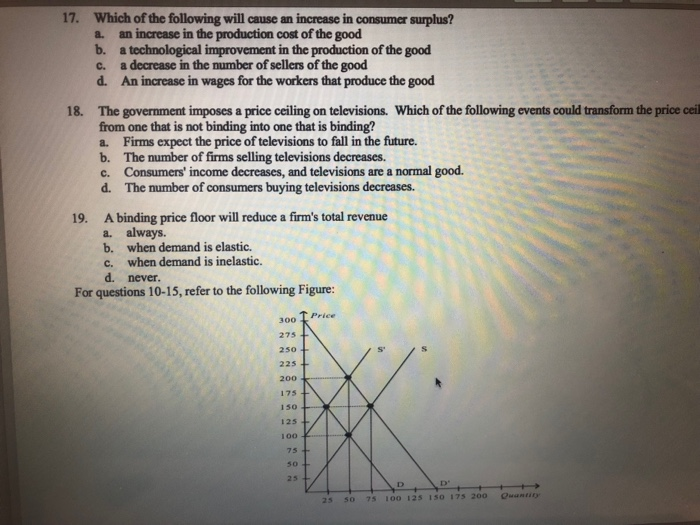
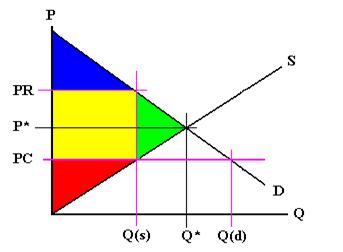
Price and quantity controls. A inefficiently low quality b inefficient allocation of sales among sellers c wasted resources d the temptation to break the law by selling below the legal price. When quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded a surplus exists. Total surplus with a binding price floor 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 p q price floor b b b b b b b a b c e d f g price floor.
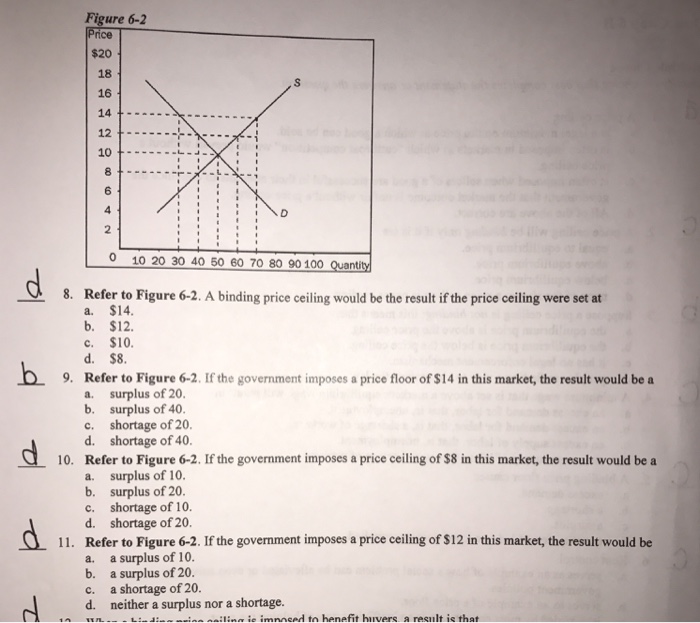
A binding price floor occurs when the government sets a required price on a good or goods at a price above equilibrium. Minimum wage and price floors. The effect of government interventions on surplus. A binding price floor is a required price that is set above the equilibrium price.
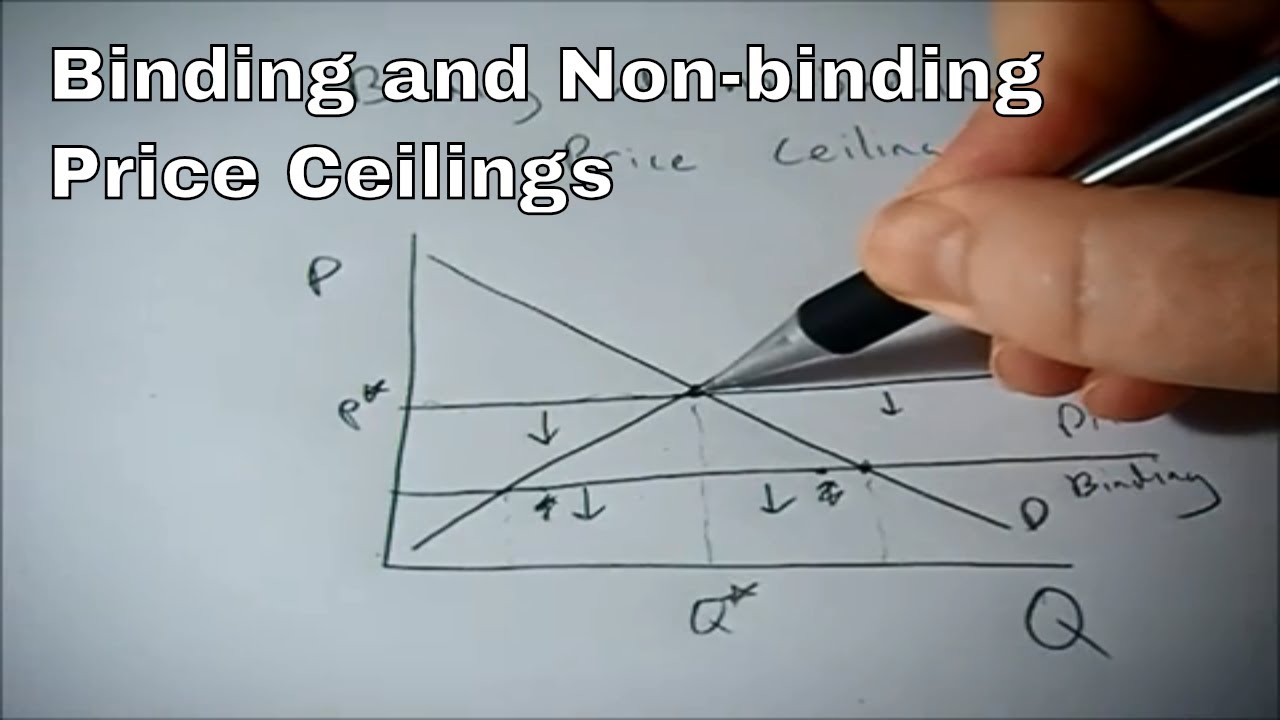
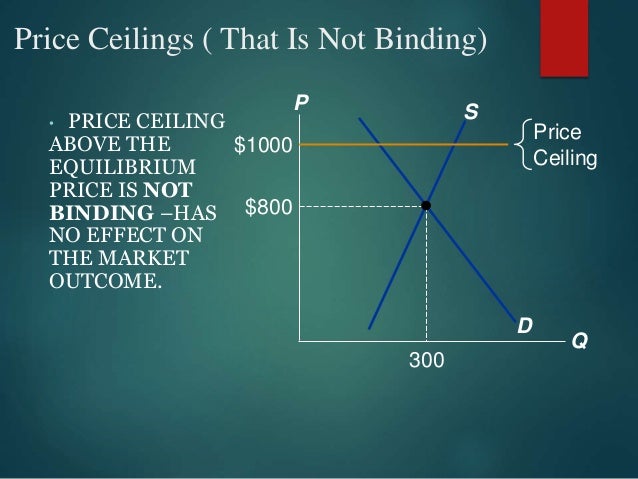
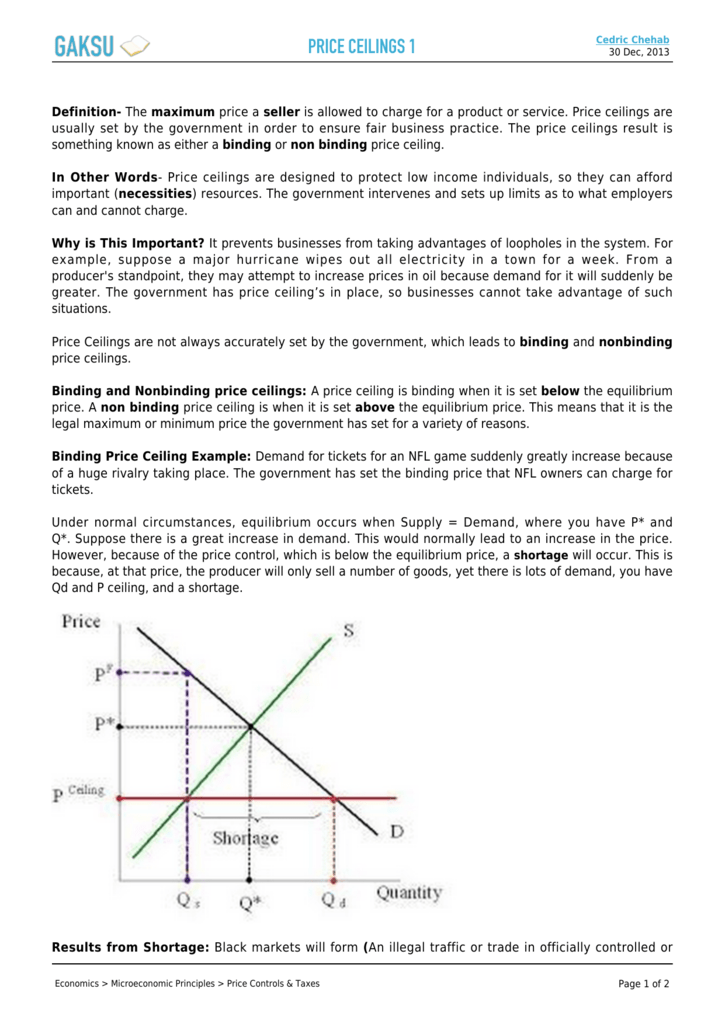
In this case the price floor has a measurable impact on the market. A price floor is an established lower boundary on the price of a commodity in the market. Another way to think about this is to start at a price of 100 and go down until you the price floor price or the equilibrium price. Qs 1 5714 0 7857p demand.
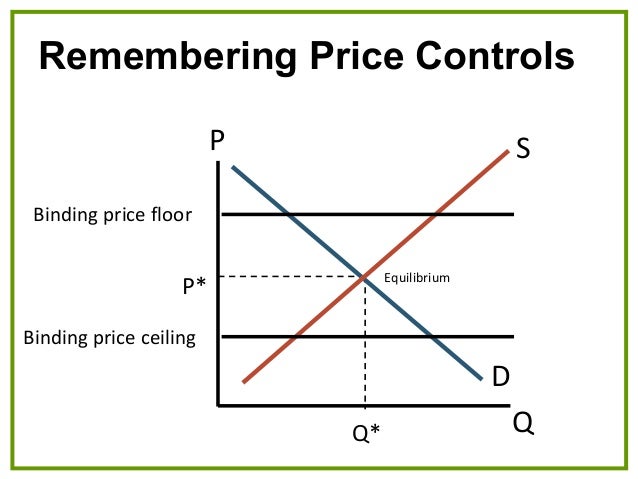
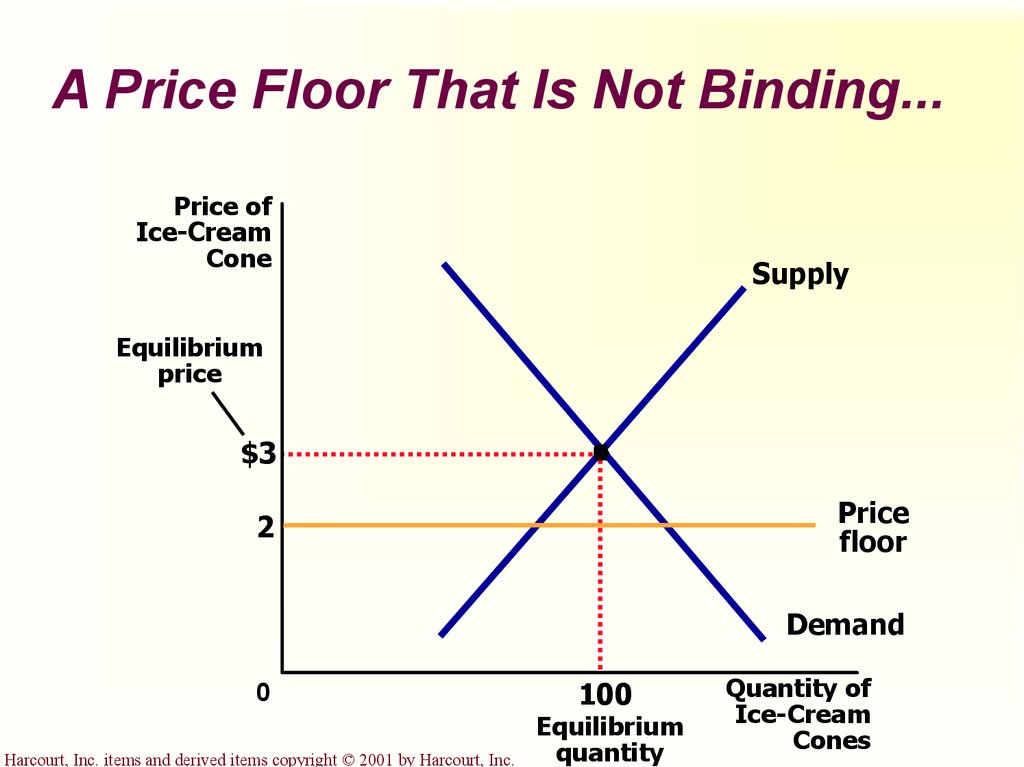
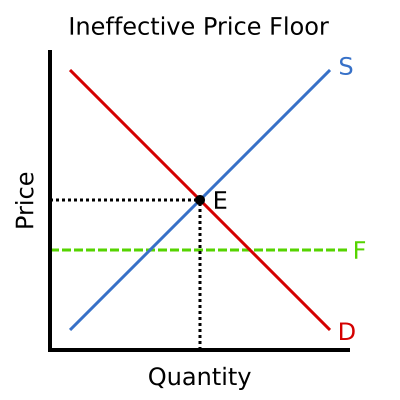
Note that the price floor is below the equilibrium price so that anything price above the floor is feasible. By contrast in the second graph the dashed green line represents a price floor set above the free market price. Example breaking down tax incidence. Governments usually set up a price floor in order to ensure that the market price of a commodity does not fall below a level that would threaten the financial existence of producers of the commodity.