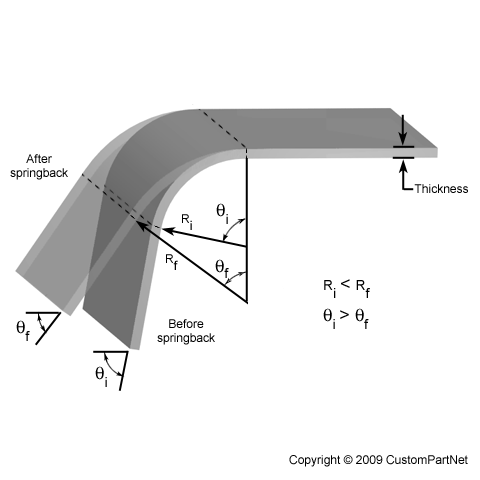
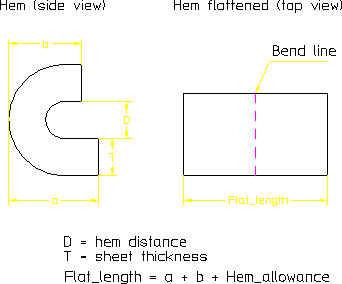
Deformation Of Sheet Metal Based On Thickness
In bulk forming the input material is in billet rod or slab form and a considerable increase in the surface to volume ratio occurs in the formed part.
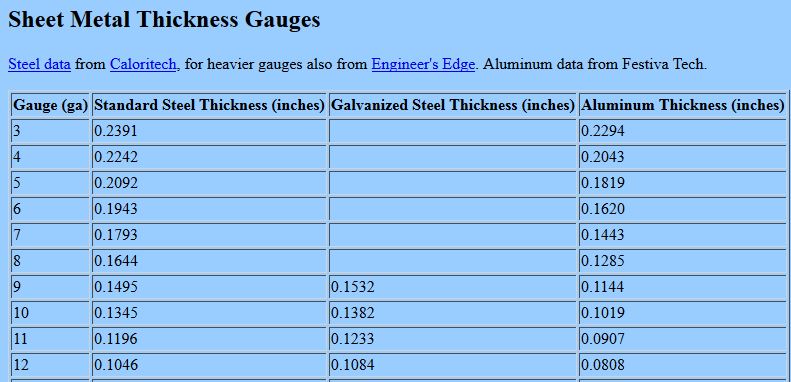
Deformation of sheet metal based on thickness. For sheet metal parts the thickness is the same everywhere. Sheet metal fabrication is a cold processing process which is commonly used for punching bending drawing and forming. Sheet metal is one of the fundamental forms used in metalworking and it can be cut and bent into a variety of shapes countless everyday objects are fabricated from sheet metal. The more ductile the metal the greater the thickness of the burnish relative to total sheet thickness.
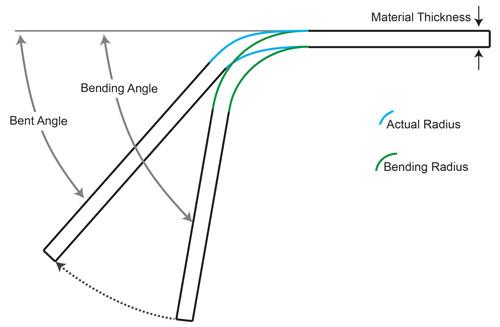
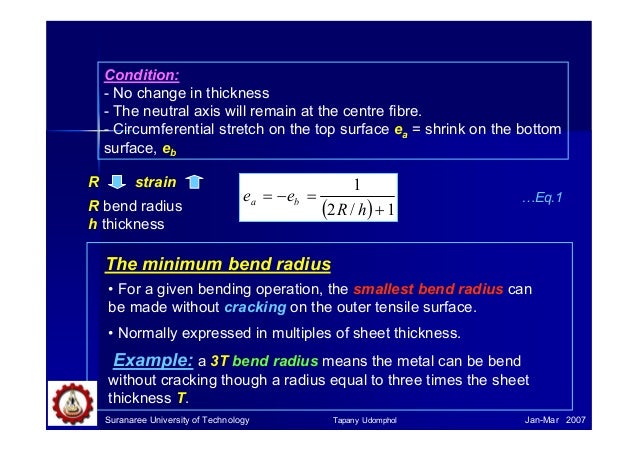
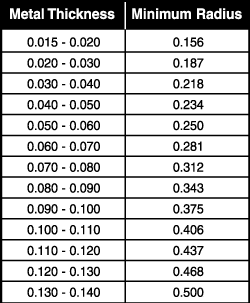
Mishra in friction stir processing for enhanced low temperature formability 2014. Basically the k factor offsets the neutral line to provide a flat pattern that reflects reality. By using it you get the bend allowance which is in essence the length of the curved neutral axis. Deformation can be reduced although not prevented entirely by paying attention to.
Increases in clearance or total sheet thickness will decrease the percent of burnish region. Extremely thin sheets are considered foil or leaf and pieces thicker than 6 mm 0 25 in are considered. Sheet metal forming is quite common for making shaped components from soda cans to automotive car bodies. It varies according to material its thickness bend radius and bending method.
Because this book is limited to bend forming which is the. Thicknesses can vary significantly. In sheet forming a sheet blank is plastically deformed into a complex three dimensional configuration usually without any significant change in sheet thickness and surface characteristics. Sheet metal usually refers to a thin metal plate with a thickness of 6 mm or less.
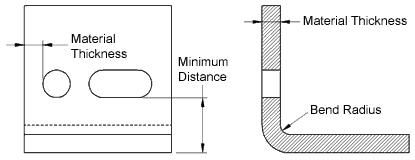
Sheet metal parts with a minimum of 0 9mm to 20mm in thickness can be manufactured. At the point of greatest stress concentration fracture takes place. Hardness and thickness variation. It is customary to refer to a material below the thickness of 6 35 mm as a sheet and thicker materials as plate.
Sheet metal is metal formed by an industrial process into thin flat pieces. Rolling metal into sheet form at the mill elongates the metal crystals and gives it a grain. Burnish zones on the hole in the sheet metal occur at the top. When designing parts for laser cutting one should not make holes smaller than the thickness of the material.
It extends into metal for about 5 to 40 of metal thickness.